IBM i RESOURCES
What is the difference between RAID and Mirroring?
While RAID improves performance and redundancy using multiple drives, while mirroring duplicates data on two drives for security. Both are essential for protecting business-critical data.
This is a common question.
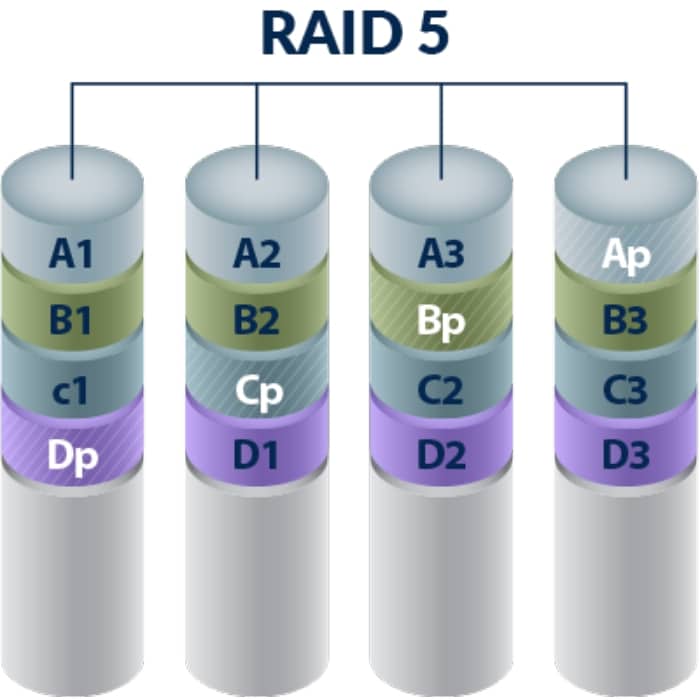
When computer people talk about RAID, they generally refer to RAID-5. RAID-5 includes a rotating parity array. (This means if there are 4 disks in an array, data is written to 3 of the disk units and space on the 4th drive is used for parity – or a way to validate the data so that if a drive in the array fails, the data can be reconstructed on the remaining 3 drives.) Thus, all read and write operations can be overlapped. RAID-5 stores parity information but not redundant data (but parity information can be used to reconstruct data). RAID-5 requires at least three and usually five disks for the array. It’s best for multi-user systems in which performance is not critical or which do few write operations.

Mirroring is another form of RAID – RAID-1 for the purist. Mirroring consists of at least 2 disk drives that duplicate the storage of data. More frequently, you will see 2 or disk units on each array so duplicate data is sent to the second array of disks. As such, if 1 disk drive fails in the first array, the system fails over to the second array of functional drives so the system can continue to operate. This gives you continuous operation while you wait to have the failed drive repaired and re-instate Mirroring.
Mirroring generally is faster for reads and can be slightly faster for writes.
Source Data Products You Might Be Interested In

Save $5,000-$80,000+ on your next IBM i Power Server upgrade. Expert migration ensures top performance, reliability, and seamless transitions for AS400 systems.

IBM i upgrades North America-wide.
Minimize risk and disruption.
Easy & stress-free system transition.
IBM i experts since 1979.
Secure & redundant cloud hosting.
Easy migration, reliable performance.
Proven and affordable.
Rapid recovery in minutes, not days.
Expert hosting, unequalled reliability.

Providing IBM i Customers with Solutions & Expertise Since 1979.
Source Data Products offers reliable, cost-effective solutions for IBM i, AS400, and iSeries systems. With over four decades of experience, we deliver expert cloud hosting, upgrades, and disaster recovery.
Complete this template for your free assessment.




